
If these are stronger than those between the solute molecules when it is solid, dissolving will take place. An ionic compound is formed by the reaction of a metal with a non-metal, whereas a molecular compound is usually formed by the reaction of two or more non. When dissolved, there will be intermolecular forces between the molecules of solute and the molecules of solvent. Classifying compounds as ionic or covalent If a compound is made from a metal and a non-metal, its bonding will be ionic. Ionic bonds form when two or more ions come together and are held together by.

When a metal and non-metal form an ionic molecule the metal will retain the element name and the non-metal will taken the suffix -ide. Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between two or more atoms. These bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. Ionic substances, on the other hand, are those that have ionic bonds between ions. Examples of molecular substances include water (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), and methane (CH 4 ). I have omitted talking about entropy here which also has a role - depends how much depth you want to go into.įor molecular solids, the force we must overcome is the intemolecular forces between the molecules. The naming of ionic compounds is dependent upon the type of ionic molecule formed from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals or transition metals. These bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, resulting in a stable molecule. Ionic solids, such as sodium chloride and nickel oxide, are composed of positive and negative ions that are held together by electrostatic attractions, which can be quite strong (Figure 10.39.

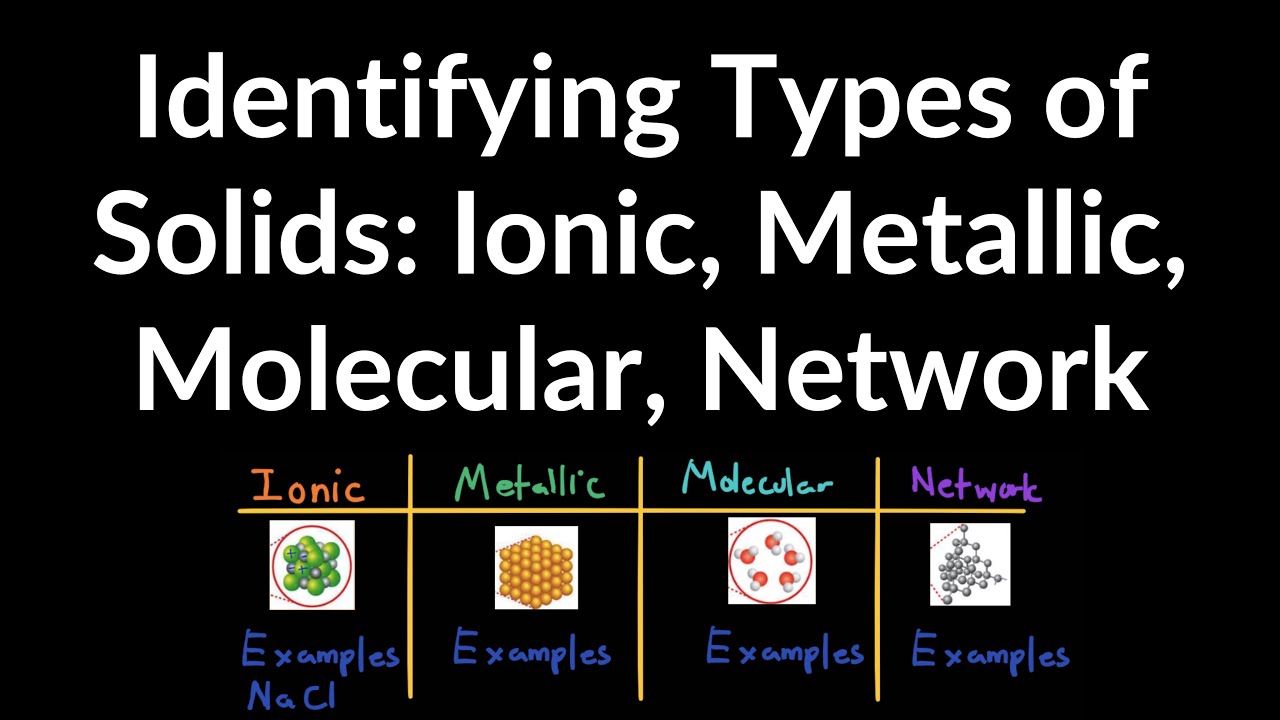
When they dissolve, the ions form bonds with the solvent molecules, and the energy released when this occurs is more than the energy needed to overcome the electrostatic attractions in the ionic lattice. The following sections provide descriptions of the major types of crystalline solids: ionic, metallic, covalent network, and molecular. If we consider ionic solids first, then what is holding them together is the electrostatic attraction between the ions. They dissolve because they are able to form more stable bonds or associations with the solvent molecules than they have holding the solid together. Binary ionic compounds typically consist of a metal and a nonmetal. Both dissolve in a similar way, but are different in the detail. Ionic and molecular compounds are named using somewhat-different methods.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
